25 Best Certifications for Remote Jobs in High-Demand Fields
With the rise of remote work opportunities, having the right certifications can significantly enhance your chances of securing a remote job in high-demand fields. Certification programs provide specialized knowledge and skills that employers value, demonstrating your expertise and commitment to professional growth. In this blog post, we will explore 25 of the best certifications for remote jobs across various industries, empowering you to thrive in the remote work landscape.
- Project Management:
Project management is the discipline of planning, organizing, and overseeing the execution of a project from start to finish. It involves applying specific knowledge, skills, tools, and techniques to meet project objectives within defined constraints, such as time, budget, scope, and quality. Project management is crucial for successful project completion and involves a structured approach to ensure efficient utilization of resources and the achievement of desired outcomes.
Key aspects of project management include:
- Project Initiation: Defining the project’s purpose, objectives, scope, and stakeholders. This phase involves conducting feasibility studies, identifying project requirements, and establishing the project’s initial parameters.
- Project Planning: Developing a comprehensive project plan that outlines the activities, timelines, resources, and deliverables. It involves creating work breakdown structures, estimating costs, identifying risks, and developing strategies to mitigate them.
- Project Execution: Implementing the project plan, coordinating resources, and performing the necessary activities to achieve the project’s objectives. This phase involves managing tasks, monitoring progress, resolving issues, and ensuring effective communication among team members.
- Project Monitoring and Control: Tracking the project’s progress, comparing it to the planned schedule and budget, and making adjustments as necessary. This phase involves monitoring project milestones, assessing performance, managing changes, and addressing deviations from the original plan.
- Project Closure: Formalizing project completion by evaluating its outcomes, documenting lessons learned, and transitioning deliverables to the appropriate stakeholders. This phase includes conducting post-project reviews, finalizing contracts, and archiving project documentation.
Project management methodologies and frameworks, such as Agile, Scrum, Waterfall, and PRINCE2, provide structured approaches to managing projects and offer specific guidelines for project managers to follow. These methodologies help optimize project workflows, enhance collaboration, and improve the chances of project success.
Effective project management requires strong leadership, excellent communication skills, stakeholder management, risk assessment and mitigation, resource allocation, and the ability to adapt to changing circumstances. Project managers play a critical role in guiding the project team, managing expectations, and ensuring the project’s successful completion.
Additionally, project management is the practice of overseeing projects and applying structured processes, methodologies, and techniques to achieve project objectives within defined constraints. It is a vital discipline across various industries and sectors, ensuring projects are completed on time, within budget, and to the satisfaction of stakeholders.
- Project Management Professional (PMP)
- Certified ScrumMaster (CSM)
- PRINCE2 Practitioner
- Digital Marketing:
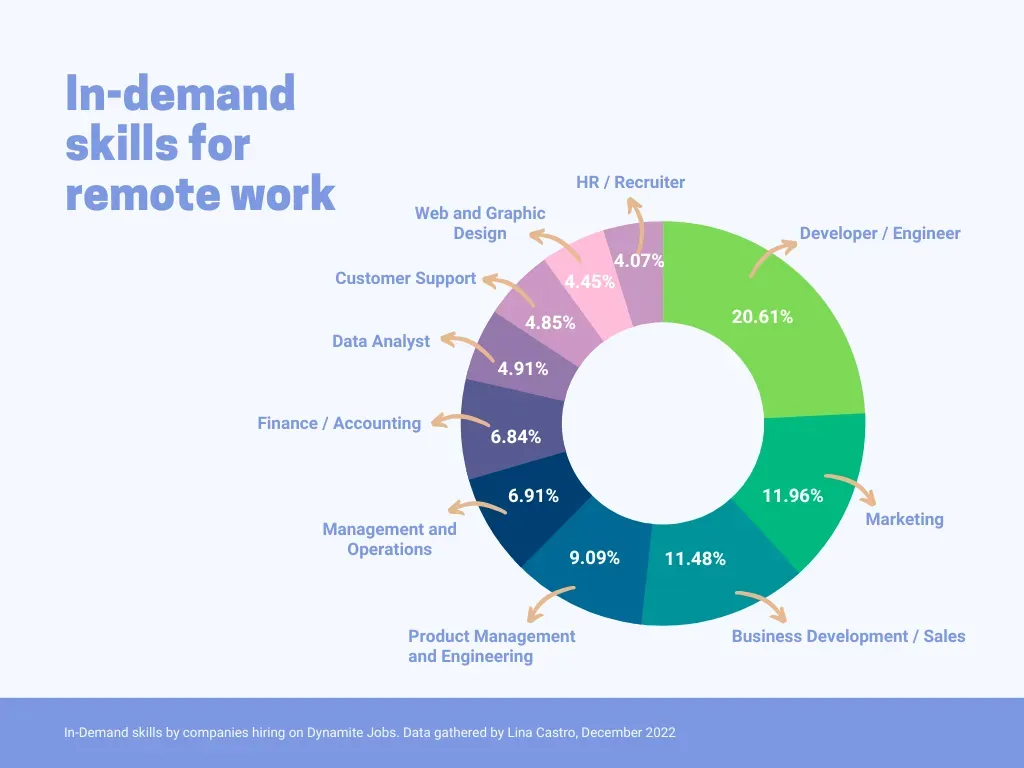
Digital marketing refers to the strategic use of digital channels and technologies to promote products, services, and brands. It encompasses various online marketing tactics and techniques that leverage digital platforms such as search engines, social media, websites, email, mobile apps, and more. Digital marketing allows businesses to reach and engage with their target audience in a more targeted and measurable way compared to traditional marketing methods.
Key Components of Digital Marketing:
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO): SEO involves optimizing websites and content to improve their visibility in search engine results pages (SERPs). It includes techniques such as keyword research, on-page optimization, link building, and improving website structure to enhance organic search rankings.
- Pay-Per-Click Advertising (PPC): PPC advertising involves placing ads on search engines or other platforms, and advertisers pay a fee each time their ad is clicked. Platforms like Google Ads and Bing Ads allow businesses to display ads based on specific keywords, demographics, and target audience preferences.
- Social Media Marketing: Social media platforms like Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, LinkedIn, and YouTube are used to promote products and services, engage with the audience, and build brand awareness. Social media marketing includes creating and sharing content, running paid advertising campaigns, and leveraging influencers to reach a wider audience.
- Content Marketing: Content marketing focuses on creating and distributing valuable and relevant content to attract and engage the target audience. It involves producing blog posts, articles, videos, infographics, and other forms of content to educate, entertain, or inspire the audience while subtly promoting products or services.
- Email Marketing: Email marketing involves sending targeted and personalized emails to a subscriber list. It is an effective way to nurture leads, build relationships with customers, promote products or services, and drive conversions. Email marketing automation tools help streamline the process and enable personalized and automated email campaigns.
- Influencer Marketing: Influencer marketing leverages the reach and influence of individuals or content creators with a significant following on social media. Brands collaborate with influencers to promote their products or services to their engaged audience, thereby increasing brand visibility and credibility.
- Mobile Marketing: With the widespread use of smartphones, mobile marketing focuses on reaching and engaging users on mobile devices through mobile apps, SMS marketing, location-based marketing, and responsive website design to ensure a seamless mobile user experience.
- Analytics and Data-driven Decision Making: Digital marketing relies on data analysis to measure the effectiveness of marketing campaigns, track key performance indicators (KPIs), and make data-driven decisions. Tools like Google Analytics provide insights into website traffic, user behavior, conversion rates, and other valuable metrics.
Digital marketing offers businesses numerous benefits, including increased brand visibility, targeted audience reach, cost-effectiveness, measurable results, and the ability to optimize campaigns in real-time. It continues to evolve as new technologies and platforms emerge, allowing marketers to adapt their strategies and tactics to stay ahead in the digital landscape.
- Google Ads Certification
- HubSpot Inbound Marketing Certification
- Facebook Blueprint Certification
- Web Development:
Web development refers to the process of creating websites and web applications. It involves designing, building, and maintaining websites using various programming languages, frameworks, and tools. Web developers are responsible for the technical aspects of website development, ensuring functionality, user experience, and responsiveness across different devices and browsers.
Key Components of Web Development:
- Front-end Development: Front-end development focuses on the client-side of web development, dealing with the visual and interactive elements that users see and interact with on a website. It involves writing HTML (Hypertext Markup Language), CSS (Cascading Style Sheets), and JavaScript code to create web pages that are visually appealing, responsive, and user-friendly.
- Back-end Development: Back-end development involves the server-side programming and logic that powers websites and web applications. It includes handling databases, server configuration, and implementing server-side scripting languages such as PHP, Python, Ruby, or Node.js to build dynamic and interactive web applications.
- Full-Stack Development: Full-stack developers are proficient in both front-end and back-end development. They have the skills to work on all aspects of web development, including designing the user interface, implementing functionality, and managing databases. Full-stack developers can handle the entire web development process independently or as part of a team.
- Web Frameworks: Web frameworks provide pre-written code libraries, tools, and components that facilitate web development and streamline the process. Popular web frameworks include Django (Python), Ruby on Rails (Ruby), Laravel (PHP), and Express.js (Node.js). These frameworks offer built-in functionalities, security features, and simplify common web development tasks.
- Content Management Systems (CMS): Content Management Systems like WordPress, Drupal, and Joomla provide platforms for building and managing websites without requiring extensive coding knowledge. They offer user-friendly interfaces, templates, and plugins that enable content creation, site customization, and functionality extensions.
- Responsive Design: With the increasing use of mobile devices, responsive design ensures that websites adapt and display correctly across various screen sizes and devices. It involves designing and developing websites with flexible layouts, fluid grids, and media queries to provide an optimal viewing experience for users on desktops, tablets, and smartphones.
- Testing and Debugging: Web developers perform testing and debugging to ensure that websites function correctly and are free of errors. This includes testing for compatibility, responsiveness, performance, security vulnerabilities, and user experience to deliver a high-quality web product.
- Web Standards and Accessibility: Web developers adhere to web standards, guidelines, and best practices to ensure compatibility across different browsers and improve accessibility for users with disabilities. Compliance with standards like HTML5, CSS3, and WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines) ensures inclusivity and usability for all users.
Web development continues to evolve with advancements in technologies and trends such as Progressive Web Apps (PWAs), Single-Page Applications (SPAs), and Application Programming Interfaces (APIs). It plays a crucial role in creating engaging, interactive, and functional websites that serve various purposes, including e-commerce, information sharing, social networking, and more.
- Certified Web Developer (W3C)
- Certified Full-Stack Web Developer (Nanodegree)
- Data Science and Analytics:
Data Science and Analytics are disciplines that involve extracting insights and knowledge from data to drive informed decision-making and solve complex problems. They encompass a range of techniques, processes, and tools used to analyze and interpret data, uncover patterns, and derive meaningful insights to support business strategies, scientific research, and various other domains.
Key Components of Data Science and Analytics:
- Data Collection and Preparation: Data scientists and analysts gather, collect, and organize relevant data from various sources such as databases, websites, sensors, or surveys. They ensure data quality, clean and preprocess it to remove inconsistencies, handle missing values, and transform it into a suitable format for analysis.
- Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA): EDA involves examining and visualizing data to understand its characteristics, relationships, and underlying patterns. This process helps identify trends, outliers, correlations, and potential insights that guide subsequent analysis.
- Statistical Analysis: Statistical techniques are applied to analyze data and draw meaningful conclusions. Descriptive statistics provide summaries and measures of central tendency, variability, and distributions. Inferential statistics help make inferences and predictions from a sample to a larger population.
- Machine Learning: Machine learning algorithms are employed to develop models that can learn from data and make predictions or classifications without explicit programming instructions. Supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning techniques are used to build predictive models, cluster data, and optimize decision-making processes.
- Data Visualization: Data visualization techniques are employed to present complex data sets in a visual and intuitive manner. Visual representations such as charts, graphs, and interactive dashboards facilitate understanding, exploration, and communication of data insights to stakeholders.
- Big Data Analytics: Big Data refers to large and complex data sets that cannot be effectively analyzed using traditional methods. Big Data analytics involves leveraging technologies like distributed computing frameworks (e.g., Hadoop, Spark) and NoSQL databases to process and analyze vast amounts of data for valuable insights.
- Data Mining: Data mining techniques explore large datasets to discover patterns, relationships, and actionable insights. It involves applying algorithms such as association rule mining, clustering, and classification to uncover hidden patterns, identify trends, and make data-driven predictions.
- Data Visualization: Data visualization techniques are employed to present complex data sets in a visual and intuitive manner. Visual representations such as charts, graphs, and interactive dashboards facilitate understanding, exploration, and communication of data insights to stakeholders.
- Data Governance and Ethics: Data governance focuses on managing and ensuring the quality, integrity, privacy, and security of data. Ethical considerations are also essential, including handling sensitive data responsibly, ensuring data privacy, and complying with legal and regulatory requirements.
Data Science and Analytics have wide-ranging applications across industries, including finance, healthcare, marketing, e-commerce, social sciences, and more. By leveraging data-driven insights, organizations can improve decision-making, optimize processes, enhance customer experiences, and gain a competitive advantage in the digital age.
- Data Science Certification (Microsoft)
- Certified Analytics Professional (CAP)
- Google Analytics Individual Qualification (GAIQ)
- Cybersecurity:
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP)
- Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH)
- CompTIA Security+
- Graphic Design:
- Adobe Certified Expert (ACE)
- Certified Professional in Graphic Design (CPGD)
- Autodesk Certified Professional (ACP)
- Content Writing and Copywriting:
- Copyblogger Certified Content Marketer
- HubSpot Content Marketing Certification
- American Writers and Artists Inc. (AWAI) Copywriting Certification
- Virtual Assistance:
- Certified Virtual Assistant (CVA)
- International Virtual Assistants Association (IVAA) Certified Virtual Assistant
- Financial Analysis:
- Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA)
- Certified Financial Planner (CFP)
- Financial Risk Manager (FRM)
- Language Translation:
- American Translators Association (ATA) Certification
- Certification in Translation (CITI)
Conclusion:
Investing in the right certifications can open doors to remote job opportunities in high-demand fields. Whether you are interested in project management, digital marketing, web development, data science, cybersecurity, graphic design, content writing, virtual assistance, financial analysis, or language translation, there are certification programs available to enhance your skills and boost your career prospects.
Remember to choose certifications aligned with your professional goals and industry requirements. Research the reputation and recognition of certification programs, and consider the time, cost, and commitment required to complete them. Certification can provide a competitive advantage and demonstrate your expertise and dedication to potential employers in the remote work landscape.
Continuously updating your skills and knowledge through certifications will not only increase your chances of securing remote job opportunities but also ensure you remain relevant and adaptable in the evolving job market. Embrace the power of certifications and unlock a world of remote work possibilities in high-demand fields. Good luck!






